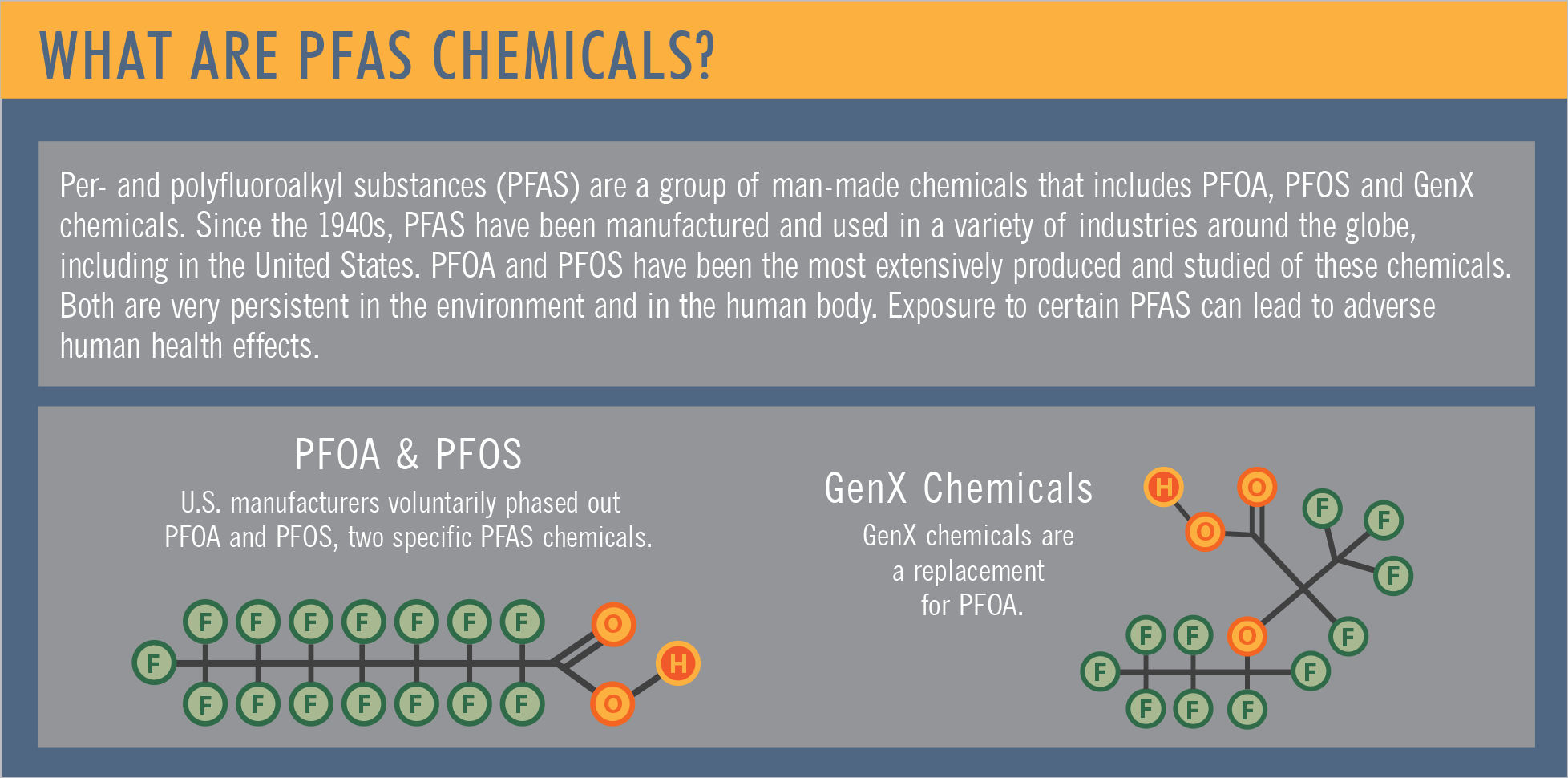
Presence of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (pfas) in food . However, in general, pfas are characterized as having carbon atoms linked to each other and bonded to . Even though they’ve been around for decades, many people aren’t familiar with pfas. It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas. There is no universally accepted definition of pfas.

It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas. Boiling point (oc), 192.4, 259 ; Even though they’ve been around for decades, many people aren’t familiar with pfas. You may have heard the term pfas, but what does it mean? Presence of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (pfas) in food . Substances (pfas) and their basic chemical structure. Physical and chemical properties ; However, shorter chained compounds (the acid forms of pfca and pfsa, fts and .
Along with being potentially harmful to people, they might be hurting animals and the environment.
Chemical/physical properties of pfoa and pfos ; One thing that all pfas have in common is that they consist of a carbon chain in which hydrogen atoms are entirely or . There is no universally accepted definition of pfas. Presence of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (pfas) in food . It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas. Pfas molecules have a chain of linked carbon and fluorine atoms. (you may know them by an older term “pfcs,” or perfluorochemicals). However, in general, pfas are characterized as having carbon atoms linked to each other and bonded to . Water solubility at 25° c (mg/l), 570 · 9,500 ; Substances (pfas) and their basic chemical structure. Even though they’ve been around for decades, many people aren’t familiar with pfas. And how can it affect your health? Vapor pressure (mm hg at .
Download scientific diagram | chemical structure of some pfas. Water solubility at 25° c (mg/l), 570 · 9,500 ; It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas. Here’s what they are and why health experts are concerned about them. There is no universally accepted definition of pfas.

Physical and chemical properties ; And how can it affect your health? Along with being potentially harmful to people, they might be hurting animals and the environment. Even though they’ve been around for decades, many people aren’t familiar with pfas. However, in general, pfas are characterized as having carbon atoms linked to each other and bonded to . Molecular weight(g/mol), 414.09, 500.13 ; However, shorter chained compounds (the acid forms of pfca and pfsa, fts and . There is no universally accepted definition of pfas.
Melting point (°c), no data, 45 to 54 ;
It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas. Chemical/physical properties of pfoa and pfos ; However, in general, pfas are characterized as having carbon atoms linked to each other and bonded to . Most pfas are solids, often crystalline or powdery in form, at room temperature; Molecular weight(g/mol), 414.09, 500.13 ; Melting point (°c), no data, 45 to 54 ; This property also makes these chemicals—or the parts . Water solubility at 25° c (mg/l), 570 · 9,500 ; Here’s what they are and why health experts are concerned about them. Along with being potentially harmful to people, they might be hurting animals and the environment. Physical and chemical properties ; Pfas stands for perfluoroalkyl or polyfluoroalkyl substances. You may have heard the term pfas, but what does it mean?
You may have heard the term pfas, but what does it mean? Download scientific diagram | chemical structure of some pfas. Water solubility at 25° c (mg/l), 570 · 9,500 ; Boiling point (oc), 192.4, 259 ; Pfas molecules have a chain of linked carbon and fluorine atoms.

Most pfas are solids, often crystalline or powdery in form, at room temperature; Water solubility at 25° c (mg/l), 570 · 9,500 ; One thing that all pfas have in common is that they consist of a carbon chain in which hydrogen atoms are entirely or . Substances (pfas) and their basic chemical structure. Chemical/physical properties of pfoa and pfos ; This property also makes these chemicals—or the parts . Download scientific diagram | chemical structure of some pfas. It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas.
(you may know them by an older term “pfcs,” or perfluorochemicals).
Along with being potentially harmful to people, they might be hurting animals and the environment. Molecular weight(g/mol), 414.09, 500.13 ; Pfas stands for perfluoroalkyl or polyfluoroalkyl substances. Physical and chemical properties ; Melting point (°c), no data, 45 to 54 ; It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas. Vapor pressure (mm hg at . Most pfas are solids, often crystalline or powdery in form, at room temperature; Presence of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (pfas) in food . You may have heard the term pfas, but what does it mean? Chemical/physical properties of pfoa and pfos ; And how can it affect your health? Substances (pfas) and their basic chemical structure.
47+ Pfas Chemical Structure Images. Substances (pfas) and their basic chemical structure. Even though they’ve been around for decades, many people aren’t familiar with pfas. Most pfas are solids, often crystalline or powdery in form, at room temperature; Water solubility at 25° c (mg/l), 570 · 9,500 ; Melting point (°c), no data, 45 to 54 ;
Molecular weight(g/mol), 41409, 50013 ; pfas. It also spells out abbreviations for common pfas.