With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mensch Innere Organe Bild: A Comprehensive Guide to the Human Internal Organs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Mensch Innere Organe Bild: A Comprehensive Guide to the Human Internal Organs
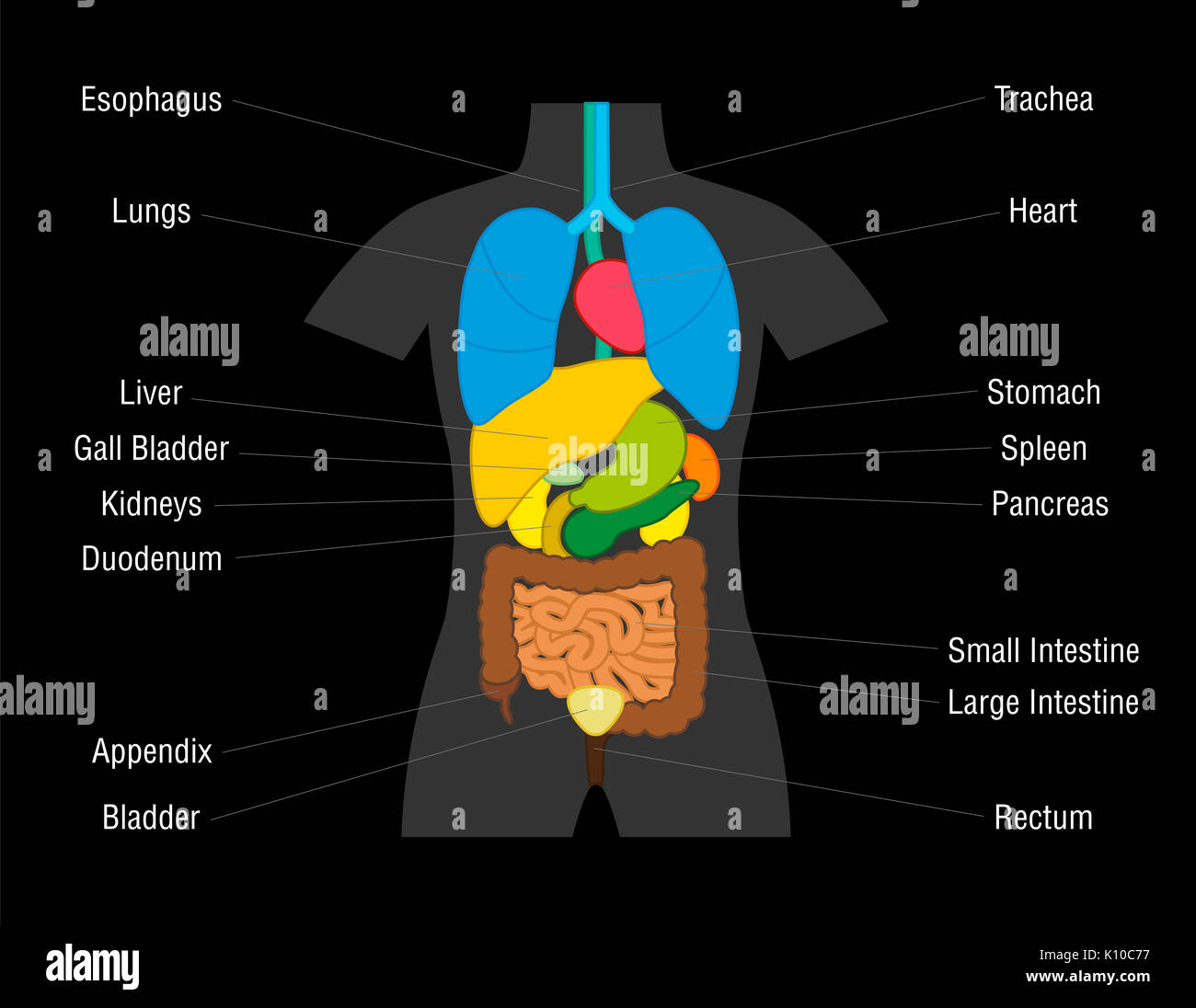
Introduction
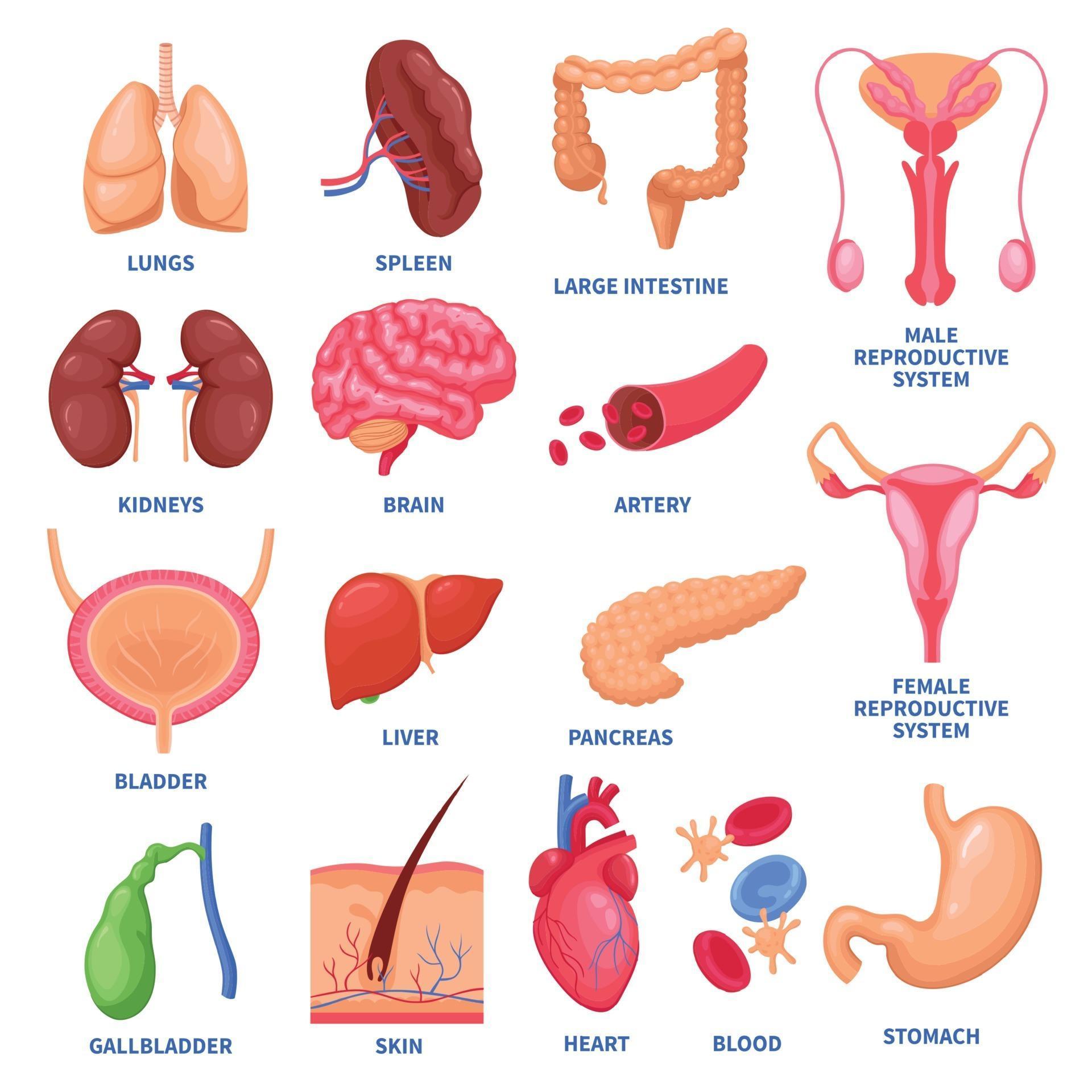
Delving into the intricate world of human anatomy, we encounter a fascinating array of organs that work harmoniously to sustain life. Understanding these internal structures is crucial for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to enhance their overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the anatomy, functions, and significance of the human internal organs, providing a deeper appreciation for the incredible complexity and resilience of the human body.
Subheading 1: The Respiratory System
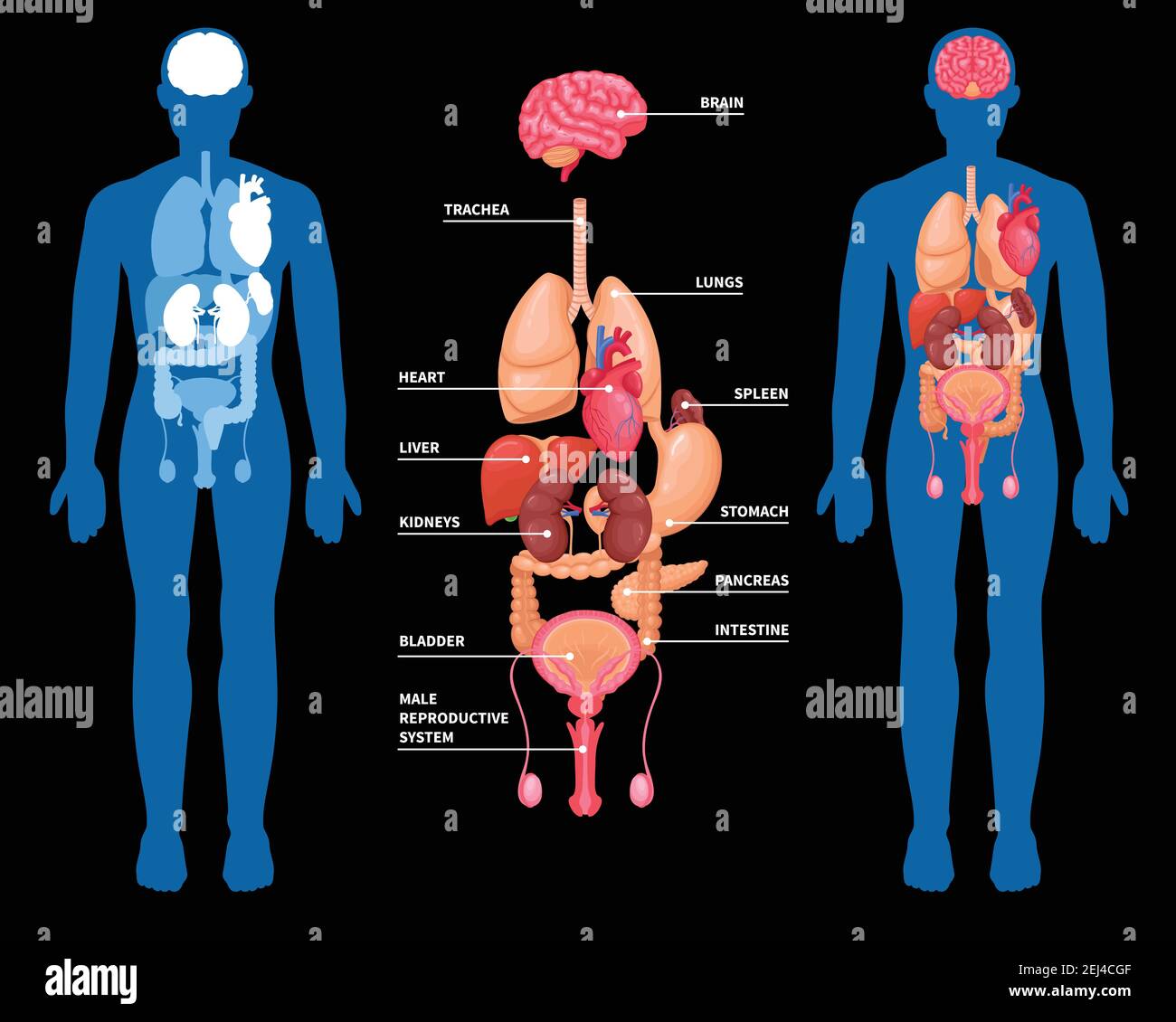
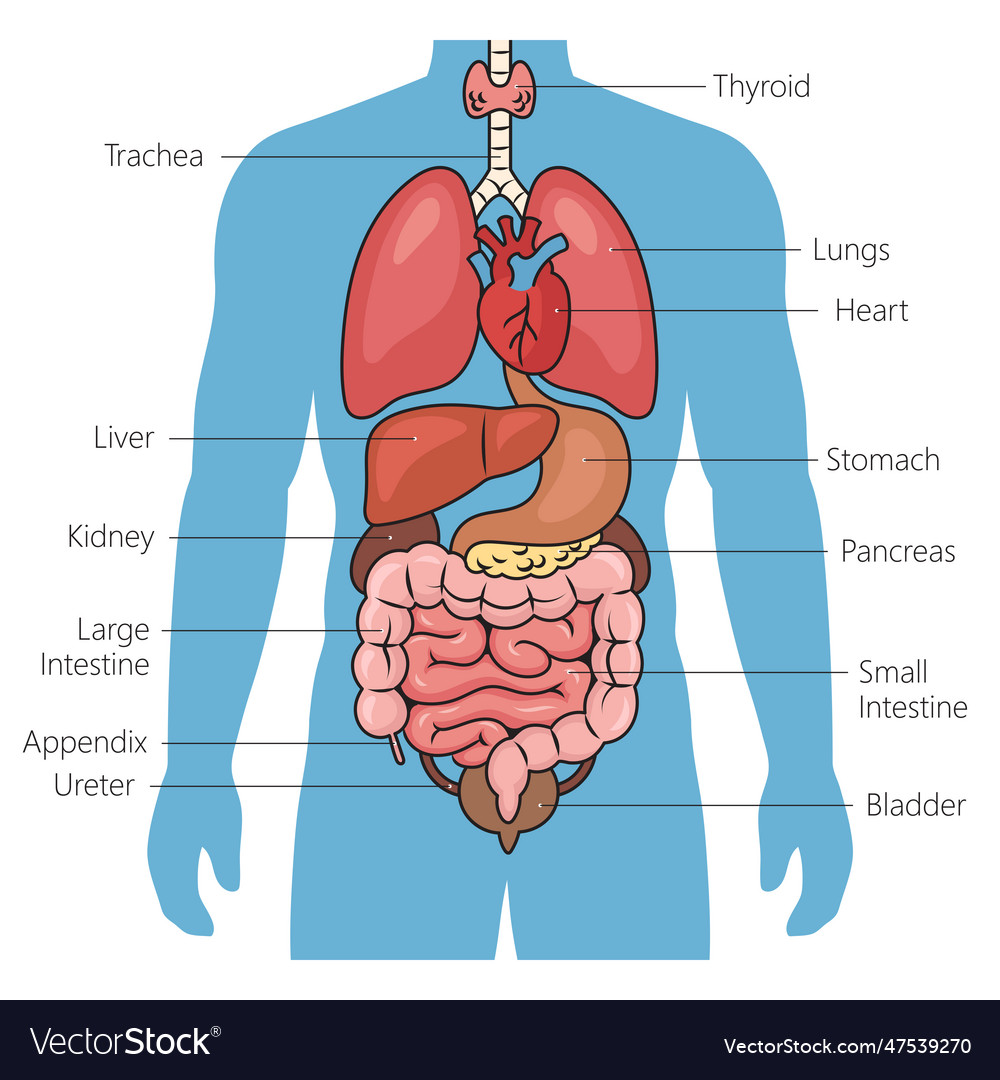
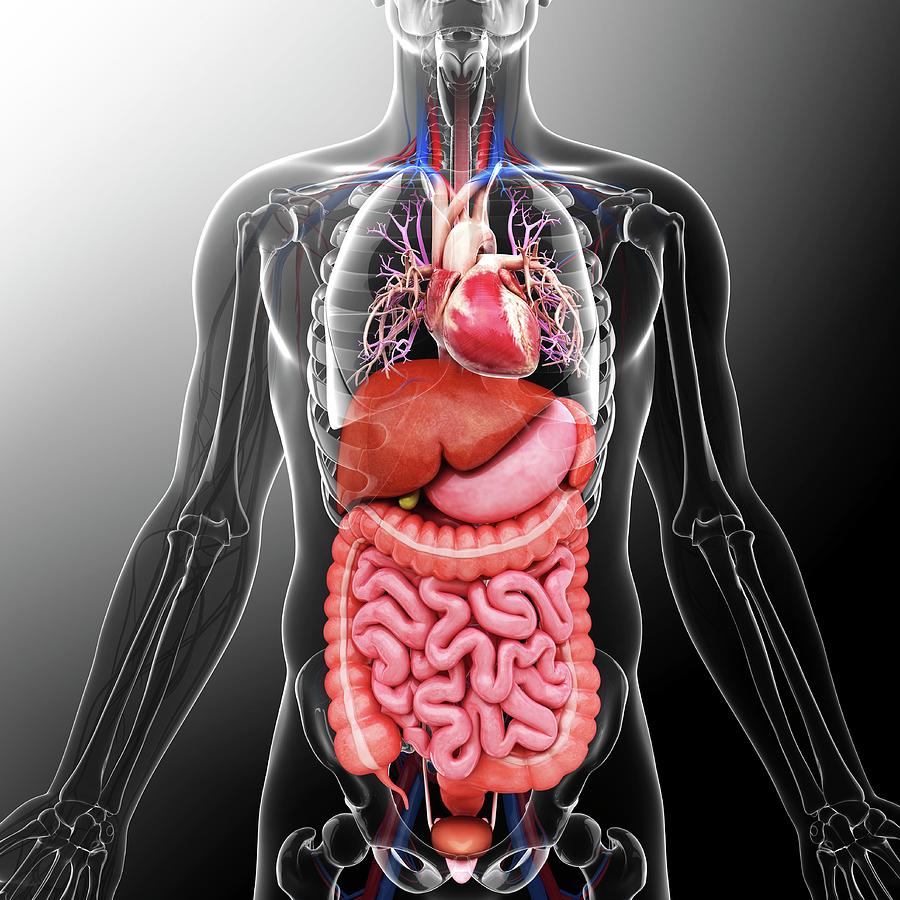
The respiratory system, a vital component of the human body, comprises the lungs, airways, and diaphragm. This intricate network facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, ensuring the proper functioning of all bodily systems. The lungs, located in the thoracic cavity, serve as the primary organs of respiration, exchanging gases through millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Subheading 2: The Cardiovascular System
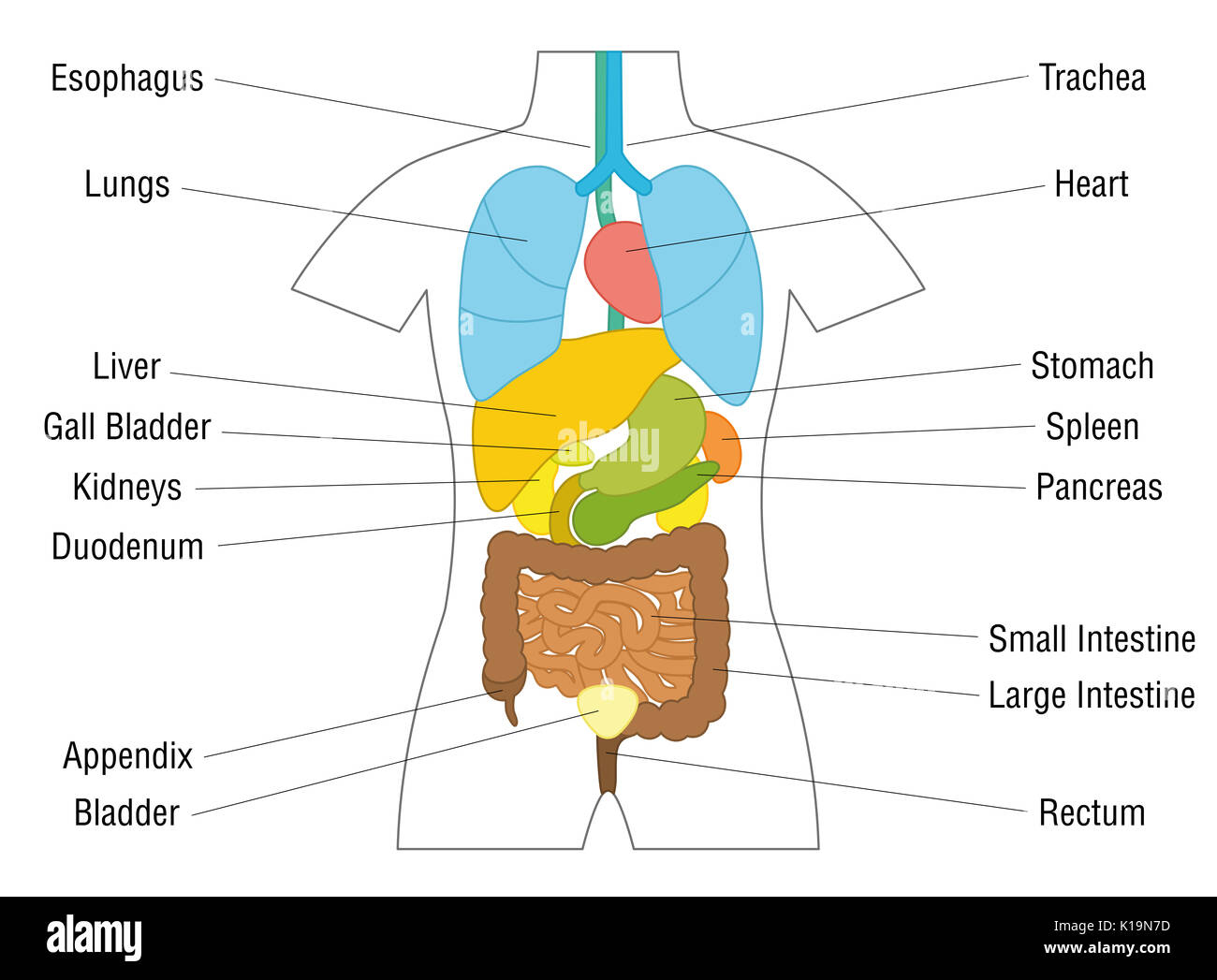
The cardiovascular system, a complex network of blood vessels, pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells while removing waste products. The heart, a muscular organ located in the chest cavity, acts as the central pump, propelling blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Subheading 3: The Digestive System
The digestive system, a series of organs and glands, plays a crucial role in breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum work together to process food, extracting essential nutrients while eliminating waste.
Subheading 4: The Urinary System
The urinary system, comprising the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. The kidneys, located near the middle of the back, perform the vital function of filtering blood, removing excess water, salts, and toxins.
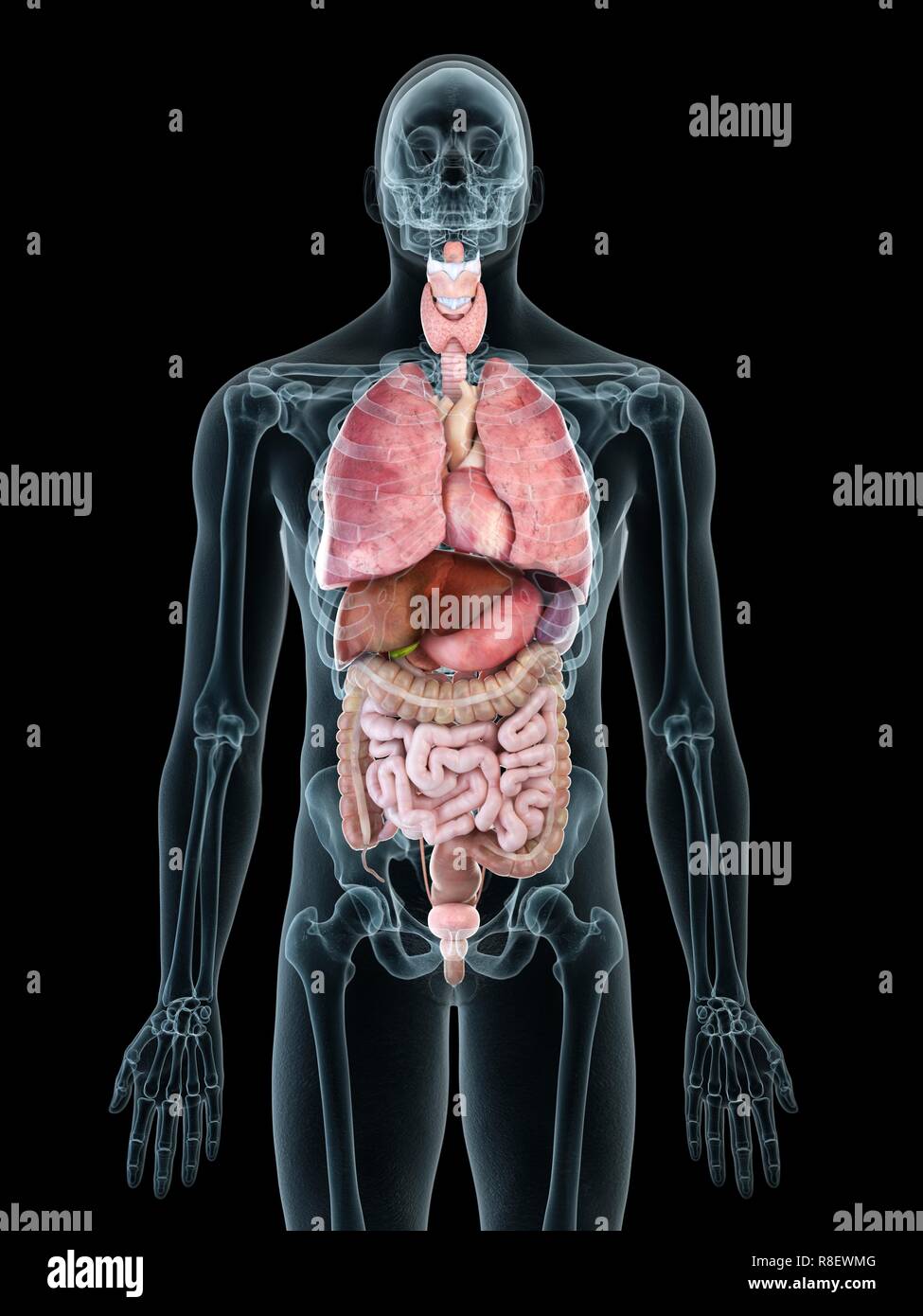
Subheading 5: The Reproductive System
The reproductive system, consisting of the reproductive organs and glands, ensures the continuation of the human species. In males, the reproductive system includes the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and penis. In females, the reproductive system comprises the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
Subheading 6: The Nervous System
The nervous system, a complex network of nerves and specialized cells, controls all bodily functions, from simple reflexes to complex cognitive processes. The brain, spinal cord, and nerves transmit electrical and chemical signals, enabling communication between different parts of the body.
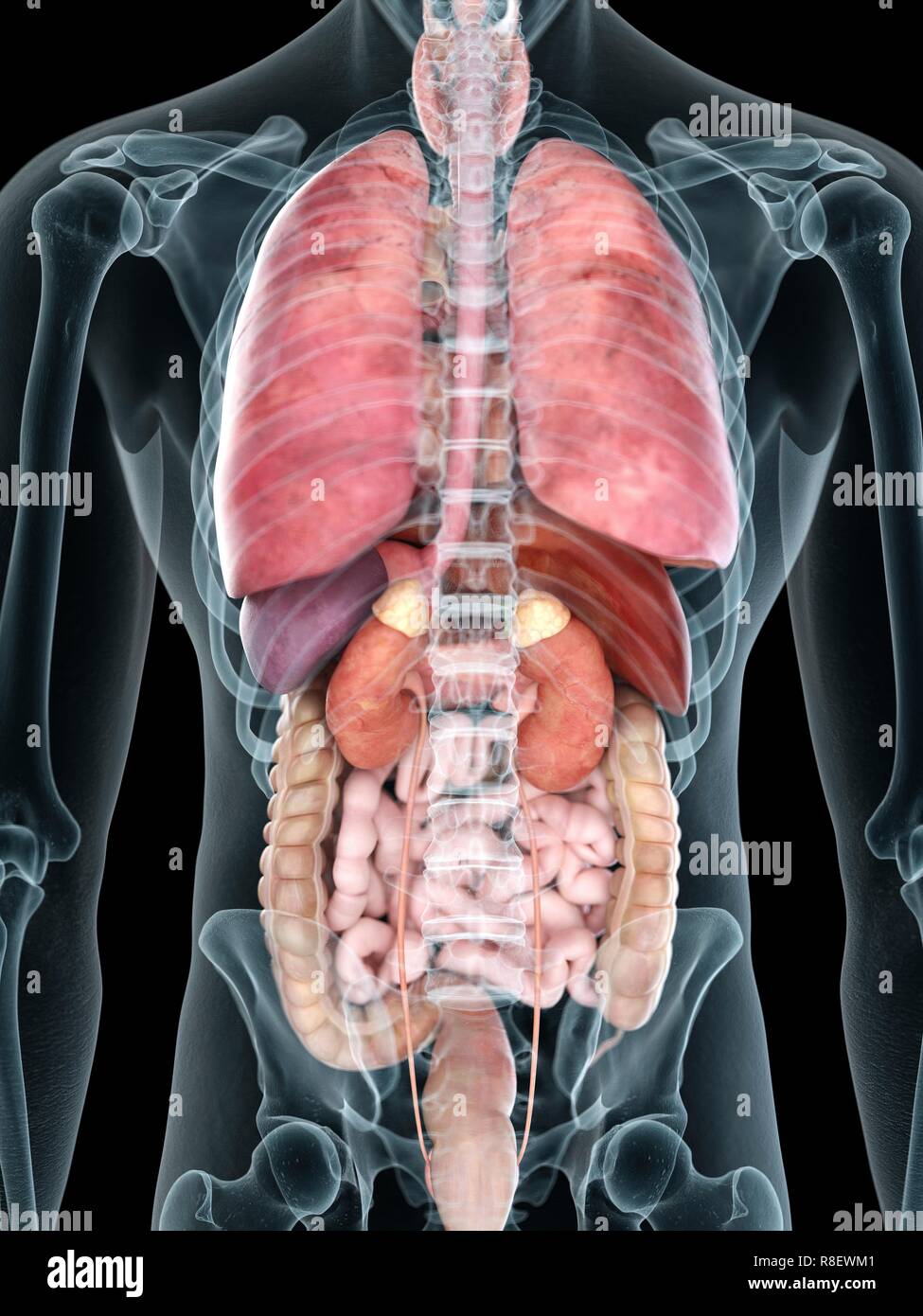
Subheading 7: The Endocrine System
The endocrine system, composed of glands that secrete hormones, regulates various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. The pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pancreas are among the most important endocrine glands, releasing hormones that influence a wide range of physiological processes.
Subheading 8: The Lymphatic System

The lymphatic system, a network of vessels and nodes, plays a crucial role in the body’s defense against infection. Lymph nodes, located throughout the body, filter out bacteria and other harmful substances, while lymphatic vessels transport lymph fluid, a clear fluid containing white blood cells.

Subheading 9: The Integumentary System
The integumentary system, consisting of the skin, hair, and nails, serves as a protective barrier against the external environment. The skin, the largest organ of the body, provides a waterproof covering, regulates body temperature, and protects against harmful UV radiation.
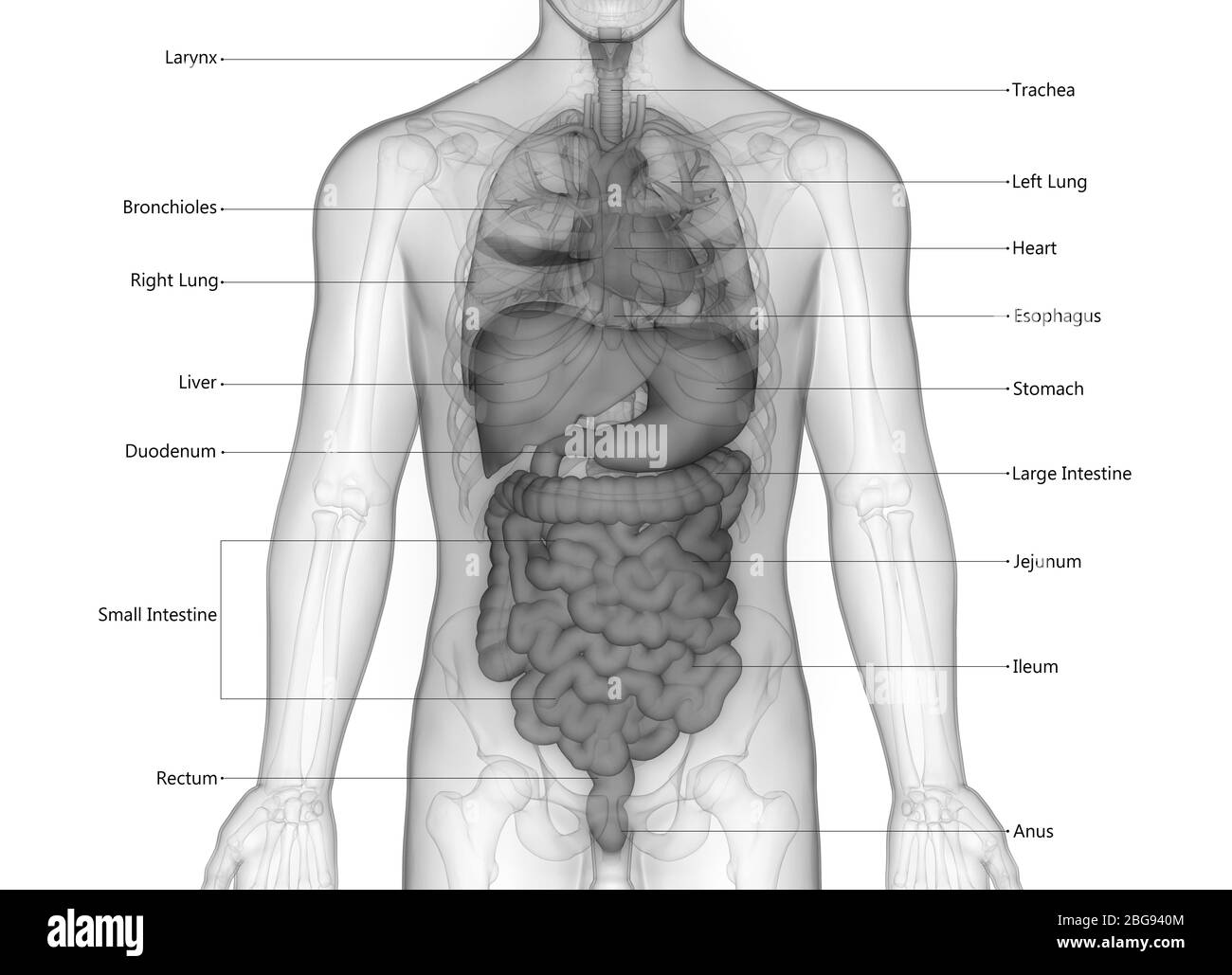
Subheading 10: The Musculoskeletal System

The musculoskeletal system, a combination of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, provides support, movement, and protection for the body. Bones, the hard structures that make up the skeleton, provide structural support and protect vital organs. Muscles, attached to bones, enable movement and generate heat.
Subheading 11: Advantages of Studying Mensch Innere Organe Bild

Understanding the human internal organs offers numerous advantages, including:

- Improved Health Literacy: Knowledge of internal organs enhances understanding of health conditions and treatments.
- Enhanced Medical Decision-Making: Informed individuals can actively participate in discussions about their health and make informed decisions.
- Increased Appreciation for the Human Body: Studying internal organs fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexity and resilience of the human body.

Subheading 12: Disadvantages of Studying Mensch Innere Organe Bild
While studying internal organs offers benefits, it may also present certain disadvantages:
- Complexity and Detail: The human body is highly complex, and understanding internal organs requires significant time and effort.
- Potential for Misinformation: Inaccurate or outdated information can lead to confusion and misunderstandings.
- Emotional Distress: Learning about certain medical conditions or diseases may evoke emotional distress.
Subheading 13: Summary of Mensch Innere Organe Bild
The human internal organs are a marvel of nature, performing vital functions that sustain life. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and significance is essential for overall well-being and medical decision-making. However, studying internal organs requires dedication and reliable information sources to avoid potential disadvantages.
Subheading 14: Q&A on Mensch Innere Organe Bild
Q1: What is the largest internal organ in the human body?
A1: The liver is the largest internal organ, weighing approximately 3 pounds.
Q2: Which organ is responsible for filtering blood?
A2: The kidneys are responsible for filtering blood and removing waste products.
Q3: What is the function of the pancreas?
A3: The pancreas secretes enzymes that aid in digestion and produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
Q4: Which organ pumps blood throughout the body?
A4: The heart is the muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
Q5: What is the role of the lymphatic system?
A5: The lymphatic system helps fight infection and drains excess fluid from tissues.
Conclusion
Exploring the intricacies of the human internal organs provides a profound appreciation for the incredible complexity and resilience of the human body. Understanding these vital structures empowers individuals to make informed health decisions, fostering a deeper connection to their own physical well-being. By embracing the knowledge of mensch innere organe bild, we unlock a world of insights that can enhance our lives and inspire a greater sense of gratitude for the wonders within us.
Closing Statement
The human body is a testament to the marvels of nature, and understanding its internal organs is a journey of discovery and empowerment. Embracing the knowledge of mensch innere organe bild not only enhances our health literacy but also fosters a profound appreciation for the intricacies of life itself. Let us continue to explore the wonders within us, unlocking the secrets that hold the key to our well-being and longevity.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mensch Innere Organe Bild: A Comprehensive Guide to the Human Internal Organs. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
