Please share to download
- Wallpaper: endometriosis pathophysiology
- Trends German
- December 14, 2022
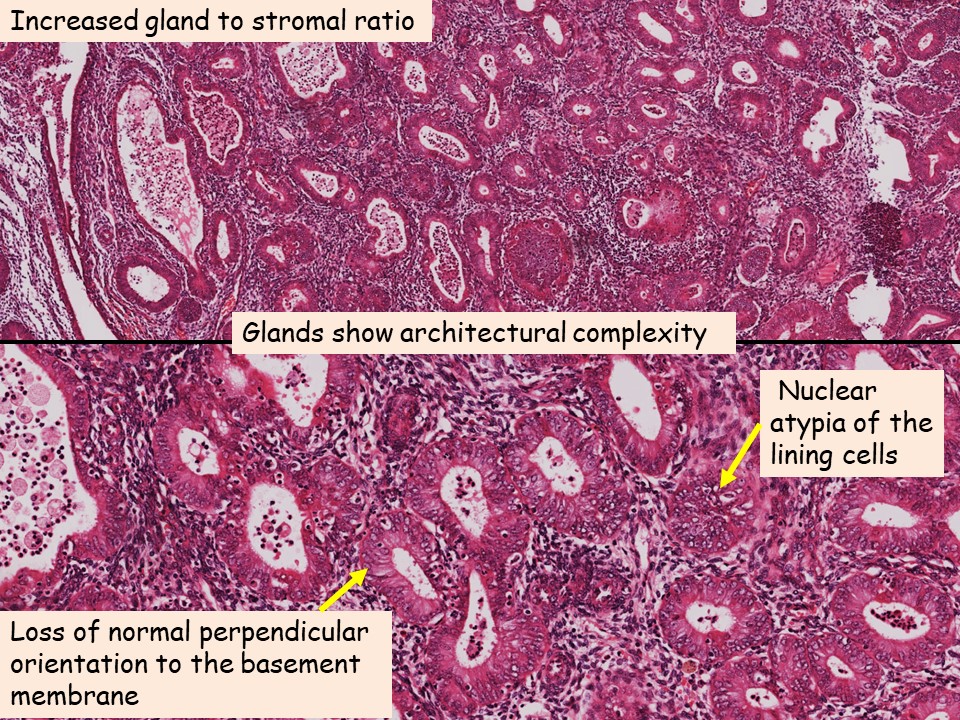
425k views 5 years ago. Endometriosis is a gynecological condition that affects approximately 11% of individuals between the ages of 15 to 44 in the united states. Viable endometrial fragments are driven through the fallopian tubes by retrograde menstruation owing to a pressure gradient originating possibly from . Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity. Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations, or locations other than the interior of the uterus.
425k views 5 years ago. Endometriosis (em) and adenomyosis (am) are common conditions with pain and infertility as the principal symptoms. Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus grow outside of the uterus, often causing discomfort, especially during your period. Viable endometrial fragments are driven through the fallopian tubes by retrograde menstruation owing to a pressure gradient originating possibly from . While there is no conclusive evidence of specific pathophysiology of depression, the national center for biotechnology information suggests that the bodily stress of major depressive disorder may cause minor or major physical disability. In someone who does not have endometriosis, endometrial tissue normally builds up within the uterine. Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity. Although endometriosis is a benign disorder, the process by which endometrial cells attach and invade surfaces shares features of malignancy. The most widely accepted hypothesis for the pathophysiology of endometriosis is that endometrial cells are transported from the uterine cavity during . The lesions are typically located in the pelvis but can occur at multiple sites including the bowel, diaphragm, and pleural cavity. Endometriosis may affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the tissue l. Previous theories suggest that endometriosis results from the transport of viable endometrial cells through retrograde menstruation. Originally described over three hundred years ago, endometriosis is classically defined by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in . Endometriosis is a gynecological condition that affects approximately 11% of individuals between the ages of 15 to 44 in the united states. Previous theories suggest that endometriosis results from the transport of viable endometrial cells through retrograde menstruation. Originally described over three hundred years ago, endometriosis is classically defined by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in . Viable endometrial fragments are driven through the fallopian tubes by retrograde menstruation owing to a pressure gradient originating possibly from . The most widely accepted hypothesis for the pathophysiology of endometriosis is that endometrial cells are transported from the uterine cavity during .
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations, or locations other than the interior of the uterus. The most widely accepted hypothesis for the pathophysiology of endometriosis is that endometrial cells are transported from the uterine cavity during . Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus grow outside of the uterus, often causing discomfort, especially during your period. Previous theories suggest that endometriosis results from the transport of viable endometrial cells through retrograde menstruation. The lesions are typically located in the pelvis but can occur at multiple sites including the bowel, diaphragm, and pleural cavity. Endometriosis may affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the tissue l. 425k views 5 years ago. Endometriosis (em) and adenomyosis (am) are common conditions with pain and infertility as the principal symptoms. Although endometriosis is a benign disorder, the process by which endometrial cells attach and invade surfaces shares features of malignancy. While there is no conclusive evidence of specific pathophysiology of depression, the national center for biotechnology information suggests that the bodily stress of major depressive disorder may cause minor or major physical disability. Endometriosis is a gynecological condition that affects approximately 11% of individuals between the ages of 15 to 44 in the united states. In someone who does not have endometriosis, endometrial tissue normally builds up within the uterine. Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity. The lesions are typically located in the pelvis but can occur at multiple sites including the bowel, diaphragm, and pleural cavity. Although endometriosis is a benign disorder, the process by which endometrial cells attach and invade surfaces shares features of malignancy. Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations, or locations other than the interior of the uterus. Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity. Endometriosis (em) and adenomyosis (am) are common conditions with pain and infertility as the principal symptoms.
425k views 5 years ago. The lesions are typically located in the pelvis but can occur at multiple sites including the bowel, diaphragm, and pleural cavity. While there is no conclusive evidence of specific pathophysiology of depression, the national center for biotechnology information suggests that the bodily stress of major depressive disorder may cause minor or major physical disability. Viable endometrial fragments are driven through the fallopian tubes by retrograde menstruation owing to a pressure gradient originating possibly from . The most widely accepted hypothesis for the pathophysiology of endometriosis is that endometrial cells are transported from the uterine cavity during . Originally described over three hundred years ago, endometriosis is classically defined by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in . In someone who does not have endometriosis, endometrial tissue normally builds up within the uterine. Endometriosis may affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the tissue l. Previous theories suggest that endometriosis results from the transport of viable endometrial cells through retrograde menstruation. Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus grow outside of the uterus, often causing discomfort, especially during your period. Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations, or locations other than the interior of the uterus. Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity. Endometriosis is a gynecological condition that affects approximately 11% of individuals between the ages of 15 to 44 in the united states. Get Endometriosis Pathophysiology Pics. The most widely accepted hypothesis for the pathophysiology of endometriosis is that endometrial cells are transported from the uterine cavity during . Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that lines the inside of the uterus grow outside of the uterus, often causing discomfort, especially during your period. Originally described over three hundred years ago, endometriosis is classically defined by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in . Endometriosis is a gynecological condition that affects approximately 11% of individuals between the ages of 15 to 44 in the united states. The lesions are typically located in the pelvis but can occur at multiple sites including the bowel, diaphragm, and pleural cavity.Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations, or locations other than the interior of the uterus.
Viable endometrial fragments are driven through the fallopian tubes by retrograde menstruation owing to a pressure gradient originating possibly from .
Although endometriosis is a benign disorder, the process by which endometrial cells attach and invade surfaces shares features of malignancy.
Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of endometrial glands and stroma outside the uterine cavity endometriosis. Endometriosis is a gynecological condition that affects approximately 11% of individuals between the ages of 15 to 44 in the united states.